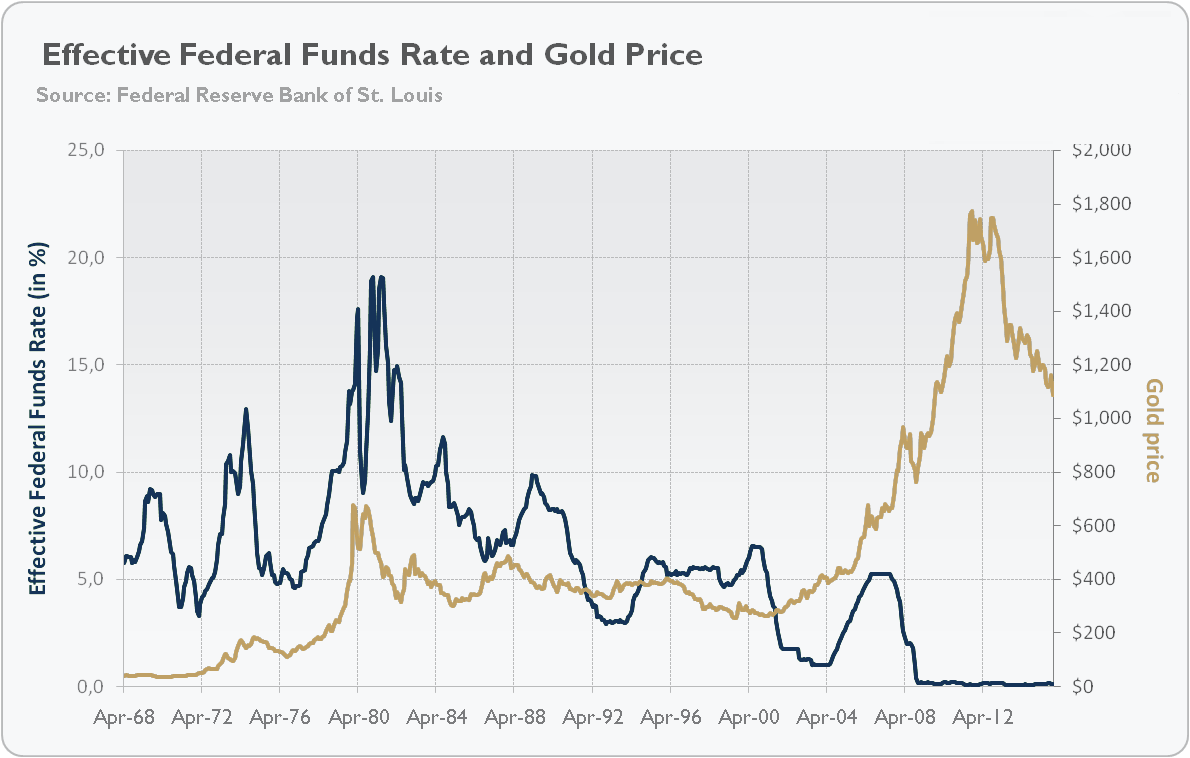
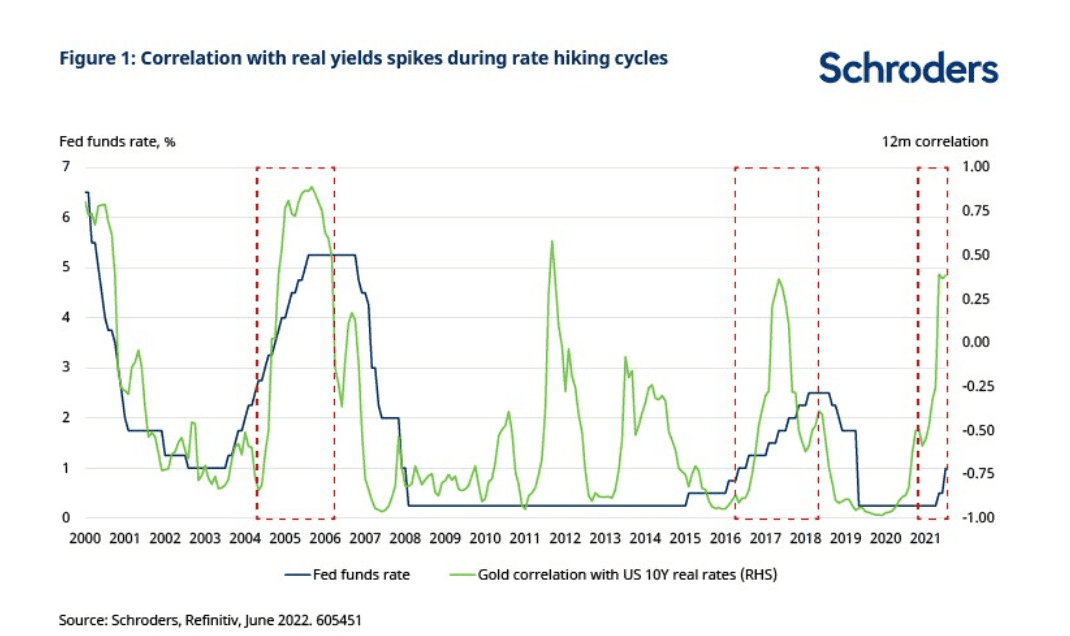
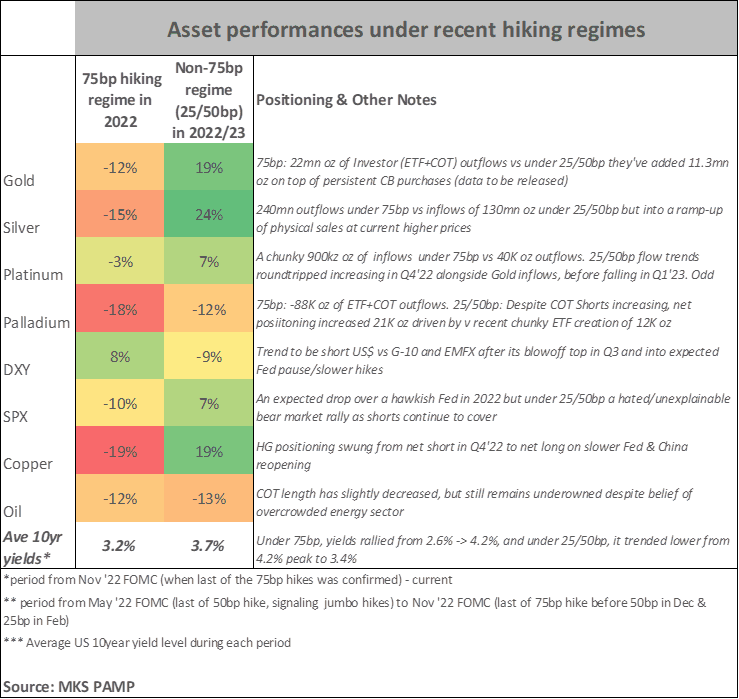
How Slower Fed Rate Hikes Could Affect the Price of Gold

The U.S. Federal Reserve has decided to slow down its interest rate hikes because it seems like high inflation has started to calm down a bit. This decision may have an impact on the price of gold, and we'll have to see how it all plays out.